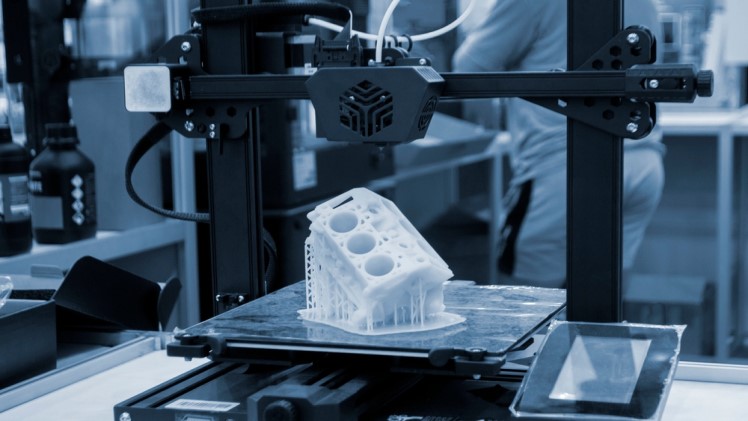
3D printing has revolutionized the way we approach making things, offering unprecedented opportunities for customization, creativity, and small-scale manufacturing. Whether you’re a hobbyist looking to bring your ideas to life or a budding entrepreneur seeking to launch a small business or side hustle, 3D printing provides an accessible and versatile toolset. Among the various 3D printing technologies, Fused Deposition Modelling (FDM) and Polyjet stand out for their distinct advantages and applications. Let’s explore how these two methods can be used at home and compare their relative costs.
Harnessing 3D Printing for Creativity and Business
Before diving into the technical differences between FDM and Polyjet, it’s essential to understand the broad range of applications these technologies can serve:
- Customization and Personalization: 3D printing allows for the creation of unique, personalized items, from custom phone cases and jewellery to tailored home decor. This is a goldmine for anyone looking to offer bespoke products that cater to individual tastes.
- Prototyping and Product Development: Rapid prototyping is one of the most practical uses of 3D printing. It enables you to iterate quickly on designs, test functionality, and refine products without the high costs of traditional manufacturing.
- Art and Crafting: For artists and crafters, 3D printing opens up new possibilities for creating intricate sculptures, miniatures, and custom tools that enhance their projects
- Small Batch Production: If you’re launching a small business, 3D printing can be a cost-effective way to produce limited runs of products without needing large-scale manufacturing equipment.
- Repairs and Spare Parts: 3D printing can be a lifesaver for creating replacement parts or customizing existing products to better suit your needs.
- Educational Tools and Kits: Educators and DIY enthusiasts can use 3D printing to create educational models, kits, and tools that bring complex concepts to life in a tangible way.
FDM vs. Polyjet: Which One Should You Choose?
Now, let’s compare FDM and Polyjet, the two leading 3D printing methods, to see which is better suited for your needs.
Fused Deposition Modelling (FDM)
FDM is the most widely used 3D printing technology, especially among hobbyists and small businesses. It works by extruding melted thermoplastic material layer by layer to build up the final object.
- Advantages:
- Cost-Effective: FDM printers are relatively inexpensive, with desktop models available for a few hundred dollars. The materials (filaments like PLA and ABS) are also affordable, typically costing between $20 to $50 per kilogram.
- Durability: FDM is great for producing strong, functional parts that can be used in a variety of applications, from prototyping to creating replacement parts.
- Versatility: FDM is well-suited for larger, less detailed objects where strength is more important than surface finish.
- Disadvantages:
- Surface Finish: FDM prints often have visible layer lines, and the surface finish is generally rougher compared to other 3D printing methods.
- Resolution: FDM is less capable of producing highly detailed or intricate designs.
Polyjet
Polyjet 3D printing is a more advanced technology that jets layers of liquid photopolymer onto a build tray and cures them with UV light. This method can produce parts with very fine detail and smooth surfaces.
- Advantages:
- High Precision and Detail: Polyjet can achieve much higher resolution and detail than FDM, making it ideal for intricate designs, prototypes, and models.
- Multi-Material Printing: Polyjet printers can combine different materials and colors in a single print, allowing for complex, multi-material parts.
- Superior Surface Finish: The prints are smooth and require less post-processing, making them more suitable for products where appearance is crucial.
- Disadvantages:
- Higher Cost: Polyjet printers and materials are significantly more expensive. The printers can cost tens of thousands of dollars, and the photopolymers can range from $200 to $600 per liter.
- Complex Maintenance: Polyjet printers require more maintenance and are generally more expensive to operate, with higher energy consumption and material waste.

Cost Comparison
When it comes to cost, FDM is the clear winner for most home-based users. The lower upfront investment, combined with cheaper materials and maintenance, makes it the preferred choice for budget-conscious hobbyists and small businesses. Polyjet, on the other hand, is better suited for professionals or businesses where the higher cost can be justified by the need for high-quality, detailed prints.
The Perfect Printer for You
Both FDM and Polyjet 3D printing technologies offer unique benefits, depending on your specific needs and budget. If you’re focused on creating functional parts, prototyping, or starting a small business on a budget, FDM provides a cost-effective and versatile solution. However, if your projects demand high precision, fine detail, and a superior finish, and you’re willing to invest in the best quality, Polyjet is the way to go.
By understanding the strengths and costs of each method, you can unlock the full potential of 3D printing, whether for personal projects or to launch your own small business.